Atopic dermatitis, also known as atopic eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition. It can occur at any age, but most often begins in infancy. It often resolves within a few years – but sometimes it accompanies a person throughout their life. Atopic dermatitis is associated with other forms of allergy such as food allergy, asthma and allergic rhinitis.
How does atopic dermatitis appear?
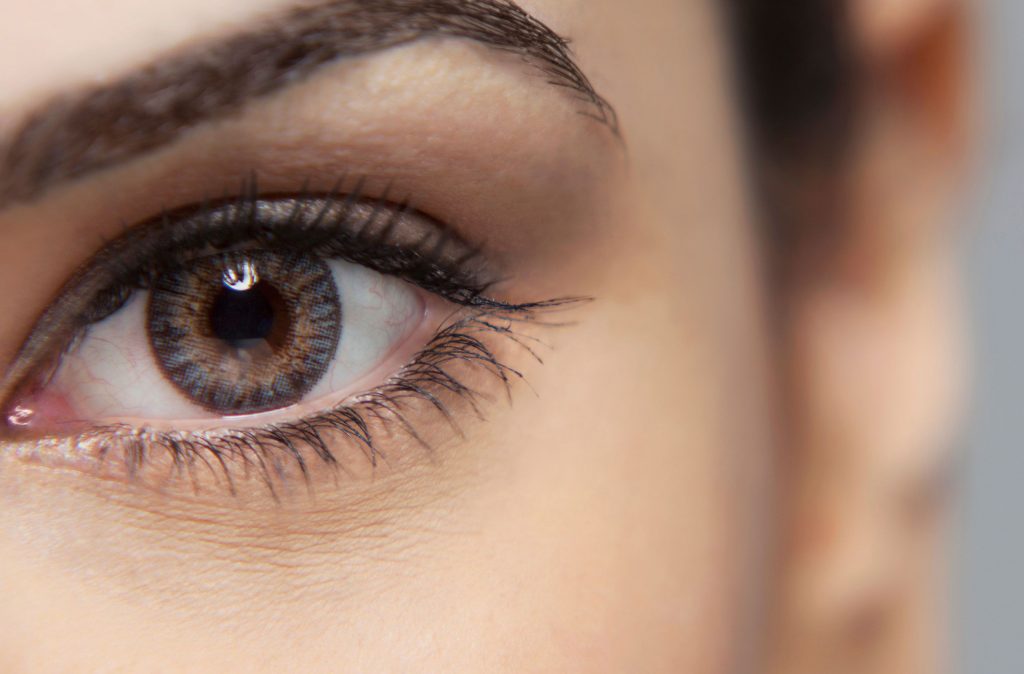
In atopic dermatitis, the skin is dry, perhaps pink or red in some areas, and there is intense itching.
Who does atopic dermatitis affect?
Atopic dermatitis usually affects 20% of infants and young children. It may persist into adulthood or appear for the first time in adulthood. In 50% of infants with atopic dermatitis, symptoms persist into adulthood.
What causes atopic dermatitis flare-ups?
Factors that can trigger an exacerbation of atopic dermatitis include humidity, cold, seasonal allergies, stress, and exposure to irritants.
What is the reason?
The cause of atopic dermatitis is not known, but the disease appears to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
What are the symptoms of atopic dermatitis?
The main symptom is itching, which can be excruciating and wake the patient up at night. The skin is also dry and red. The folds of the hands, knees, wrists, face, neck or even the entire body may show the above symptoms. Skin infections (e.g. staphylococcus) occur at an increased frequency compared to the healthy population, as a result of scratching and the defective skin barrier that patients have.
What is the prognosis of atopic dermatitis?
Although the symptoms of atopic dermatitis are unpleasant for the individual, proper and comprehensive treatment offers significant relief to patients. The aim of treatment is to keep the disease in long-term remission and to prevent flare-ups and unpleasant complications.